Antibiotics & Health
Antibiotics & Health Overview
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) has been termed the ‘silent pandemic’ as it makes it more difficult and even impossible to treat bacterial infections. In 2019, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared AMR one of the top 10 global health threats facing humanity.
It is recognised not only as a global threat to public health, but also to economic prosperity, as the global economic costs associated with AMR are likely to be US$100 trillion and lead to a long-term 3.8% decrease in GDP by 2050.
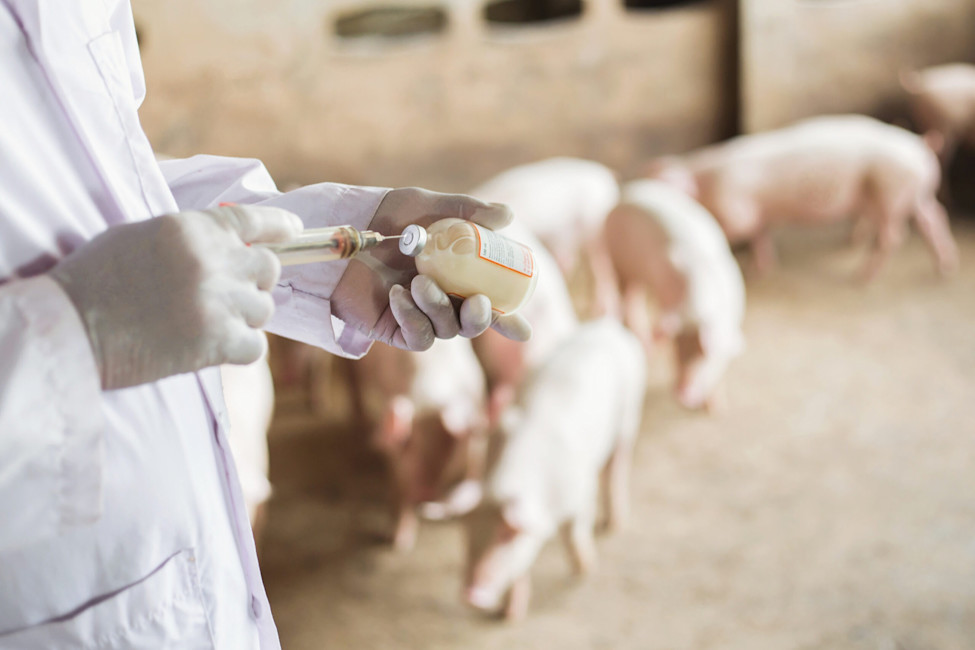
Reliance on the routine use of antibiotics in factory farming for growth promotion and prophylaxis has resulted in animal agriculture accounting for an estimated 70% of antibiotic consumption globally. The industry is consequently a significant contributor to AMR globally, with this expected to rise as more countries embrace intensive farming systems to meet the growing demand for meat, dairy and fish. It is projected that by 2030, antibiotic consumption in farm animals will increase by 67%.
As a result, FAIRR efforts seek to encourage responsible use of antibiotics in line with WHO guidelines through company engagement across the animal protein supply chain and multilateral stakeholder engagement on the issue to encourage policy change in key producing regions.

Latest Activity
Report Launch: Restaurant Antibiotics Engagement Phase 2 Progress Report
Explore key findings from Phase 2 of FAIRR’s Restaurant Antibiotics Engagement, which aimed to encourage 12 of the largest North American Quick-Service Restaurants to implement global antibiotic policies that address AMR risks across six animal protein supply chains.
Guide Launch: Health and Wealth: The Investors’ Guide to Antimicrobial Resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is recognised by investors as a risk to global health and economic stability.
Co-developed by MSCI Sustainability Institute, IAAMR and FAIRR, the guide explores strategies that investors can implement to address AMR. It provides an analysis of the economic impacts, risks and opportunities associated with AMR as well as case studies demonstrating how investors are taking action.
Research Launch: Protein & Nutrition: Research overview
This research overview provides key scientific insights into the environmental and social impacts of different protein sources, clarifies common assumptions about their health effects, and identifies trends, risks and opportunities for investors with exposure to the protein supply chain.
Knowledge Hub | Antibiotics Use in Intensive Animal Agriculture
This article explores the risks associated with the routine use of antibiotics in animal agriculture, in particular antimicrobial resistance and its broader implications for human health.
New Insight | Future-Proofing Food Investments Through Improved Animal Welfare
Animal welfare is becoming a defining investment issue. This Insight explores how rising regulation, real-world failures and supply-chain risks are reshaping expectations for food companies and what it means for long-term value.
New Insight | Could the Current Bird Flu Crisis Cause the Next Pandemic?
With the rise of avian influenza, experts warn of increasing pandemic risks. This insight examines the financial and supply chain impacts, along with how investors can future mitigate risks.
Animal Pharmaceuticals Engagement
This engagement tackles the lack of transparency from animal pharmaceutical companies over how they manufacture, market, and sell antibiotics – practices that could contribute to AMR hotspots in the environment and drive high levels of antibiotic use.
Follow
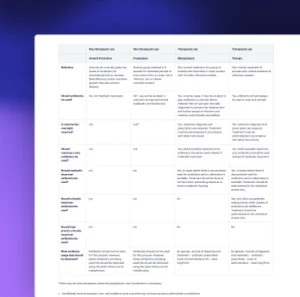
Restaurant Antibiotics Engagement
This engagement addresses the quick-service restaurant sector on the need to improve antibiotic stewardship practices.
Follow
FAIRR view: Responsible antibiotic use in animal agriculture
The responsible use of antibiotics in animal supply chains plays an integral role in preserving efficacy of antibiotics and preventing the spread of AMR.